Comparação de Comportamentos de Corrosão de Ligas de Titânio para Aplicações em Implantes Dentários: Revisão
Link: /uploads/arquivos/COMPARATIVE-CORROSION-BEHAVIOUR-OF-TITANIUM-ALLOYS-FOR-DENTAL-APPLICATIONS.pdf
Cátia S. D. Lopes , Mariana T. Donato and P. Ramgi ¹ Departamento de Química e Bioquímica, Faculdade de Ciências, Universidade de Lisboa, 1749‐016 Lisboa, Portugal, marianat.donato@gmail.com, pramgi@gmail.com *A quem a correspondência deve ser dirigida, e‐mail: csolopes@fc.ul.pt
https://www.lneg.pt/download/13313/v35n2a01.pdf
RESUMO
Atualmente existe uma necessidade crescente de materiais biocompatíveis devido à toxicidade dos metais usados. Nos implantes dentários existem vários problemas relacionados com a corrosão dos implantes, como a elevada concentração de iões fluoreto, tornando o meio ácido. Considerando que o titânio tem uma excelente biocompatibilidade e alguma resistência à corrosão, uma forma de melhorar esta propriedade é formando ligas de Ti com outros metais. A liga Ti-6Al-4V é a mais usada, apesar da sua toxicidade. Consequentemente, há necessidade de fazer novas ligas que sejam resistentes à corrosão mas menos tóxicas. Uma que se destaca é a Ti-15Mo. O objetivo desta revisão é comparar estas duas ligas em termos do comportamento à corrosão e possíveis tratamentos para melhorar a resistência à corrosão.
Palavras-chave: Ligas de Titânio, Corrosão, Implantes Dentários, Osseointegração, Tratamentos de Superfície
ABSTRACT
Nowadays there is an increasing need of biocompatible materials due to the toxicity of the metals used. Focusing in dental implants, there are several problems concerning the corrosion of implants, for example, the high concentration of fluoride ions, which make an acid medium. Considering that titanium has excellent biocompatibility and some resistance to corrosion, one way to enhance this property is alloying Ti with other metals. The most used alloy is Ti-6Al-4V, in spite of its toxicity. Hence, there is a need to make new alloys which are resistant to corrosion and less toxic. One that stands out is Ti-15Mo. The objective of this review is to compare these two alloys in terms of corrosion behaviour and possible treatments to improve their corrosion resistance. Keywords: Titanium Alloys, Corrosion, Dental Implants, Osseointegraon, Surface Treatments
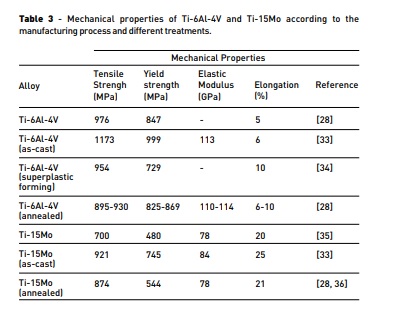
• Ti-6Al-4V Ti-6Al-4V is an alpha plus beta type alloy, in which the stabilizers are aluminium (alpha) and vanadium (beta), the nominal composition is listed in Table 4. This alloy presents great mechanical properties and high resistance to corrosion [10, 37], being one of the most used materials in dentistry. In spite of this, it has a much greater elastic modulus than bone, causing stress shielding effect [5, 38]. Adding to this, the implant is not electrochemically stable, which can undergo a process of leaching, leading to an increase of vanadium and aluminium concentration in the soft tissues [39] that can cause several diseases like osteomalacia, peripheral neuropathy and Alzheimer's disease [40- 42]. This fact presents a major concern in human health care, requiring other implants with no possible damage to human health. In this line of thinking, other alloys with non-toxic components like Mo are being developed. Table 4 - Ti-6Al-4V composition. Adapted from [32].
CONCLUSION
It is evident that it is not easy to compare all of these studies to arise at a definite answer about the better material to use. From this review there are some highlights which are important to analyse. When comparing c.p. Ti and Ti-6Al-4V, c.p. Ti presents better corrosion resistance, but Ti-6Al-4V presents better mechanical proprieties than c.p. Ti, which, for the implant to be successful, is of extreme importance. However, the dissolution of the passive layer of Ti-6Al-4V, leads to health problems, stimulating the search of other alloys with better mechanical proprieties and with no potential damage to human health.
